Opioid abuse has reached alarming levels in the United States, thus posing challenges to public health and safety. The widespread availability of prescription medications containing opioids and illegal practices have contributed to the crisis. One critical aspect of addressing this issue is understanding how long do opioids stay in your system.
To understand how long opioids stay in your system, determine the drug testing procedures employed for various reasons, such as court-ordered testing, legal cases, employee screenings, and probation-related procedures.
What Are Opioids
Opioids, whether natural opiates or synthetic, are commonly prescribed for pain relief. They attach to specific brain and spinal cord receptors, thus reducing pain perception. However, opioids can also produce euphoria and relaxation, leading to misuse and addiction. The method of administration—oral, injection, or inhalation— effects how long the substance remains in the body.
The Drug Testing Methods
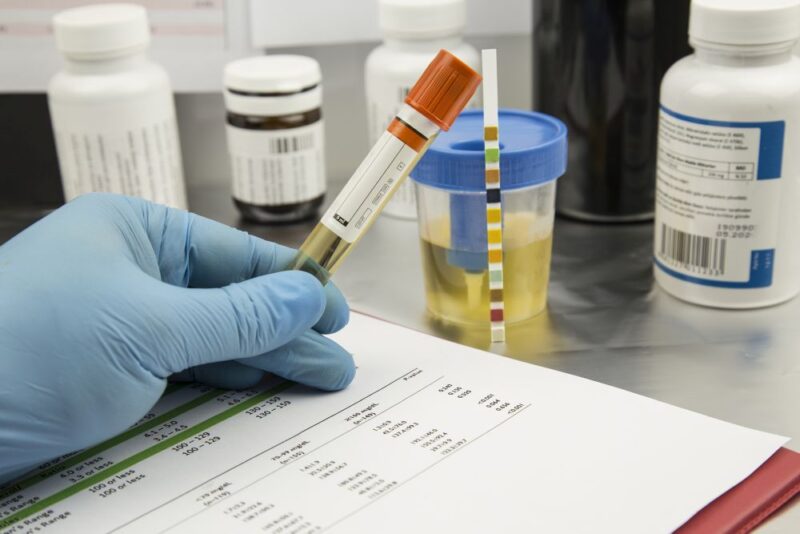
Drug tests are conducted using different methods, including urine, saliva, blood, and hair tests. Among these, urine testing is the most common testing method due to its ease, affordability, and quick results. Urine tests can detect the presence of opioids used in the past few days.
Hair testing, on the other hand, is highly effective and can reveal opioid use over a longer period, sometimes up to 90 days. The duration opioids stay in the system varies based on the specific drug, metabolism, physical activity, and other factors.
Factors Affecting Opioid Detection
Understanding how long opioids remain in the body is a complex interplay of various factors. It’s not just about the type of drug a person takes; metabolism, weight, and even physical activity determine how long do opioids stay in your system.
Short-acting opioids, for instance, leave the body system faster, whereas longer-acting ones can persist for up to 10 days or even longer. Also, the duration required for the body to eliminate half of the substance impacts how long it can be detected in tests.
Effect Of Hydration and Urine Ph Levels on Detection
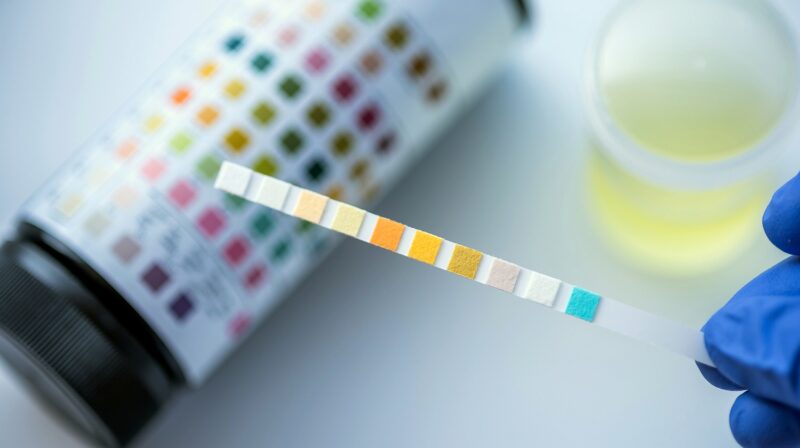
Well-hydrated individuals eliminate drugs faster, and alkaline urine pH helps eliminate drugs more rapidly. Conversely, acidic urine pH might prolong the drug’s presence in the body.
How to Prevent Opioid Abuse
Preventing opioid abuse is a collective effort that begins with awareness and responsible actions. It’s about informing communities about the potential dangers of these drugs and emphasizing the importance of securely storing prescriptions.
Following the prescribed dosage under the guidance of a physician is fundamental in ensuring medications are used as intended. Also, recognizing the subtle signs of opioid addiction is vital. If there’s even a suspicion of habit, seek help immediately.
The journey to recovery often involves a combination of approaches. Medication-assisted treatment can provide valuable support by easing the process of withdrawal and reducing cravings.
Therapy sessions offer a safe space to explore the underlying causes of addiction and develop coping mechanisms. Support groups can be incredibly empowering, where individuals share their experiences and encourage one another. Together, these treatment options form a support network that can aid recovery by reminding patients that they are not alone in their struggle.
Summary
Understanding how long opioids stay in the system is vital for effective drug testing and addiction prevention. By being informed about the detection timeframes and factors influencing opioid elimination, patients and healthcare professionals can take proactive measures to address opioid abuse and promote a healthier and safer society. If you know someone struggling with opioid addiction, advise them to seek professional help as the first step towards recovery and a drug-free life.

